GMAO RESEARCH HIGHLIGHTS, 2007-2009
Below are titles and descriptions of the GMAO Research Highlight entries from 2007 through 2009. These writeups are summaries of selected GMAO scientific research activities.
2009
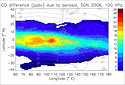 Impact of 2006 Biomass burning aerosols on tropical dynamics studied with GEOS-5
Impact of 2006 Biomass burning aerosols on tropical dynamics studied with GEOS-5A new study uses the Goddard Earth Observing System, Version 5 (GEOS-5) atmospheric general circulation model to study the impact of aerosols produced by the 2006 Indonesian fires on atmospheric temperature, moisture, and circulation in the region.
2008
 GEOS-5 - CloudSat Intercomparisons · Aug. 2008
GEOS-5 - CloudSat Intercomparisons · Aug. 2008A new study utilizes global analyses of the atmosphere obtained from the new GEOS-5 Data Assimilation System (DAS) developed for GMAO's Modern-Era Retrospective analysis for Research and Applications (MERRA) to examine the relationships between cloud parameters observed by the CloudSat satellite and predictors of convective cloud structure derived from MERRA reanalyses.
2007
 Convective Transport of Trace Gases · Nov. 2007
Convective Transport of Trace Gases · Nov. 2007Modeled transport of CO and CO2 is used to evaluate parameterizations in GEOS-5 and to identify which parameters have the greatest impact on trace gas transport in three different storms.
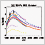 Multimodel Projections of Stratospheric Ozone in the 21st Century · Sep. 2007
Multimodel Projections of Stratospheric Ozone in the 21st Century · Sep. 2007Simulations from eleven coupled chemistry-climate models (CCMs) employing nearly identical forcings have been used to project the evolution of stratospheric ozone throughout the 21st century.
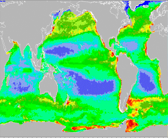 Improving Estimates of Surface Chlorophyll by Assimilation of SeaWiFS Data · May 07
Improving Estimates of Surface Chlorophyll by Assimilation of SeaWiFS Data · May 07Daily, global surface chlorophyll values for 1998 to 2004 have been estimated by assimilation of SeaWiFS data into the NASA Ocean Biogeochemical Model.
 20th Century Climate Variations in Observations and Reanalyses · Apr. 2007
20th Century Climate Variations in Observations and Reanalyses · Apr. 2007To study global warming trends and the pan-decadal variability (PDV) in the Pacific, the dominating ENSO signal is removed first. After we do this, our investigations of observations and reanalysis datasets show that the warming in the Pacific basin is weaker than surrounding basins and that one of several PDV regime shifts occurred during the 1990s.
 The Use of an OSSE to Estimate Characteristics of Analysis Error · Mar. 2007
The Use of an OSSE to Estimate Characteristics of Analysis Error · Mar. 2007A new application of OSSEs shows great promise for helping to answer fundamental questions about atmospheric analysis techniques, observation instruments, and forecast skill measures.
 Observation Sensitivity Calculations Using the Adjoint of the Gridpoint Statistical Interpolation (GSI) Analysis System · Mar. 2007
Observation Sensitivity Calculations Using the Adjoint of the Gridpoint Statistical Interpolation (GSI) Analysis System · Mar. 2007GMAO scientists have developed a new formulation of the GEOS-5 atmospheric data assimilation system to understand and improve the way observations are used in weather and climate forecasts.
 Dominant modes of instabilities in the stratosphere · Mar. 2007
Dominant modes of instabilities in the stratosphere · Mar. 2007GMAO scientists use GEOS-5 to examine the leading modes of weather instability in the stratosphere to help provide insight into observed stratospheric dynamical phenomena.
 Impact of Deep Soil Temperatures on the Atmosphere · Mar. 2007
Impact of Deep Soil Temperatures on the Atmosphere · Mar. 2007AGCM studies show that interactive deep soil temperatures significantly increase surface air temperature variability but reduce the variability of the hydrological cycle.

